Types of Orders on Pocket Option
Contents
An order is an instruction from a trader to a broker to buy or sell a financial asset. It is a key element in the trading process, allowing market participants to specify exactly what operation they want to perform, at what price, and in what volume. Orders help structure the trading process, manage risks, and implement trading strategies. Pocket Option offers traders several types of orders, each with its own features and applications:
- Trade Orders: Allow immediate execution of trades at the current market price or a specified price.
- Express Orders: Ensure fast execution of trades with minimal delays.
- Pending Orders: Enable automatic opening of positions when certain price levels are reached.
Each type of order has its advantages and is suitable for various trading situations and strategies.
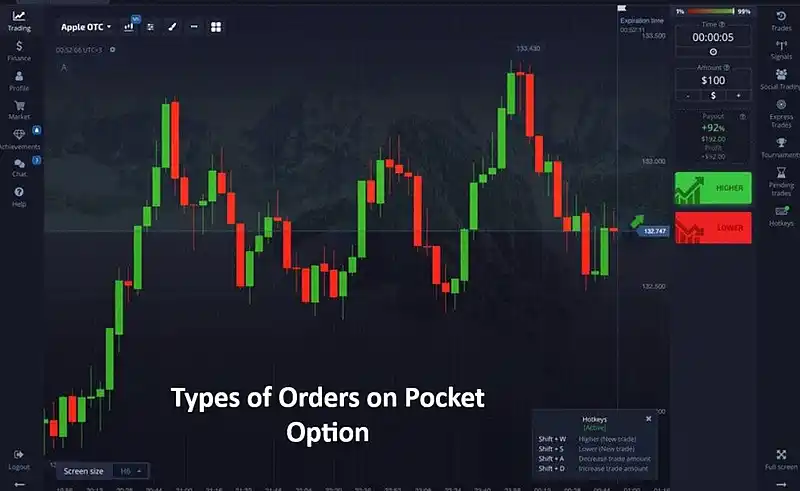
Trade Orders
Trade orders are the basic type of orders Pocket Option used for the immediate opening or closing of positions in the market. They allow traders to quickly respond to the current market situation and implement their trading ideas in real-time.
Types of Trade Orders
- Market Orders:
Executed immediately at the current market price.
Guarantee execution but do not guarantee a specific price.
Ideal for quick market entry or exit. - Limit Orders:
Executed only at the specified price or better.
Allow precise control over the entry or exit price.
May not be executed if the market does not reach the specified price.
Advantages and Disadvantages
Advantages:
- Fast execution (especially for market orders).
- Ability to control price precisely (for limit orders).
- Ease of use.
Disadvantages:
- Risk of slippage for market orders.
- Possibility of non-execution for limit orders.
- Need for constant market monitoring for optimal placement.
Trade orders are the foundation for most strategies and are suitable for both short-term and long-term trading. The choice between a market order and a limit order depends on the specific situation, the trader’s strategy, and their risk tolerance.
Express Orders
Express orders are a special type of order designed for the fastest possible execution of trades. Their main feature is minimizing the time between placing the order and its execution. This concept is especially important in highly volatile markets or when trading with a short time horizon, where every second counts.
How They Work on Pocket Option
In Pocket Option, express orders are implemented as follows:
- Priority Processing: Express orders receive priority in the execution queue.
- Optimized Routing: Special algorithms are used to select the fastest execution path.
- Minimal Checks: Only critical checks are performed to speed up the process.
- Automatic Execution: Once the order is placed, it is executed automatically without additional confirmations.
- Fixed Fees: Typically have slightly higher but fixed fees for fast execution.
Situations When They Are Most Effective
Express orders are particularly useful in the following situations:
- Scalping: For traders using strategies with very short time intervals.
- News Trading: When there is a need to quickly react to important economic news or events.
- High Volatility: During periods of sharp price fluctuations, when it’s important to quickly enter or exit a position.
- Arbitrage: To take advantage of short-term price differences between markets.
- Closing Positions: When it’s necessary to quickly close a losing position to minimize losses.
- Breakout Trading: When trading on breakouts of important levels, where entry speed is critical.
- Algorithmic Trading: In automated trading systems, where execution speed is a key factor.
Express orders are a powerful tool for traders who value execution speed. However, their use requires experience and an understanding of market dynamics, as fast execution can lead to unexpected results in rapidly changing market conditions.
Pending Orders
Pending orders are instructions to the broker to buy or sell a financial instrument in the future when a certain price level is reached. They allow traders to automate their trading decisions and respond to market changes even without active monitoring.
Types of Pending Orders
Stop Loss:
- Designed to limit losses.
- Activated when the price reaches a certain loss level.
- Automatically closes the position to prevent further losses.
Take Profit:
- Used to secure profits.
- Triggered when a specified profit level is reached.
- Automatically closes the profitable position.
Buy Stop:
- An order to buy above the current market price.
- Activated when the price breaks above a certain level.
Sell Stop:
- An order to sell below the current market price.
- Triggered when the price breaks below a certain level.
Buy Limit:
- An order to buy below the current market price.
- Executed when the price falls to a specified level.
Sell Limit:
- An order to sell above the current market price.
- Activated when the price rises to a certain level.
Strategies for Use
- Using stop loss orders to limit potential losses.
Securing Profits:
- Applying take profit orders to automatically close profitable positions.
Breakout Trading:
- Utilizing buy stop and sell stop orders to enter the market on breakouts of key levels.
Reversal Trading:
- Employing buy limit and sell limit orders to enter the market on corrections.
Automating Trading:
- Combining different types of pending orders to create automated trading strategies.
Key Characteristics of Each Order Type
| Order Type | Execution Speed | Price Guarantee | Automation | Risk of Non-Execution | Commission |
| Market | Very High | No | No | Low | Standard |
| Limit | Medium | Yes | Yes | High | Standard |
| Express | Maximum | No | No | Low | Increased |
| Stop Loss | High | No | Yes | Low | Standard |
| Take Profit | High | Yes | Yes | Medium | Standard |
| Buy Stop / Sell Stop | High | No | Yes | Medium | Standard |
| Buy Limit / Sell Limit | Medium | Yes | Yes | High | Standard |
Recommendations for Choosing an Order Type Based on the Situation
- For quick market entry/exit: Market or express order.
- When a specific price is desired: Limit order.
- To automatically limit losses: Stop loss order.
- To automatically secure profits: Take profit order.
- For breakout trading: Buy stop or sell stop order.
- When expecting a price correction: Buy limit or sell limit order.
- In high volatility conditions: Express order or a combination of market order with stop loss.
- For long-term positions: Combination of a limit order for entry with pending orders (stop loss and take profit).
- For news trading: Express order or pre-set pending orders.
- To implement complex trading strategies: Combination of various types of pending orders.
The choice of order type on Pocket Option depends on the individual trading strategy, market conditions, and the trader’s personal preferences regarding the balance between speed, execution accuracy, and level of automation.
Practical Tips
How to Properly Place Different Types of Orders:
Market Orders:
- These orders are best used during periods of stable market liquidity. Remember that a market order does not guarantee a specific execution price, so always consider possible slippage. They are particularly useful when speed is more important than the exact entry price, such as when needing to quickly close a losing position or take advantage of a sudden market opportunity.
Limit Orders:
- Place them at support or resistance levels identified through technical analysis. Consider the current trend and market volatility when choosing the order price. Be prepared for the possibility that a limit order may not be executed if the market does not reach the specified price. These orders are ideal for patient traders willing to wait for a better price.
Stop-Loss Orders:
- Set them at a level that minimizes losses but is not too close to the current price to avoid premature activation due to normal market fluctuations. Consider the average volatility of the asset over the chosen time period. Regularly review and adjust stop-loss orders as the price moves in your favor to protect already realized profits.
Take-Profit Orders:
- Base them on technical analysis and the risk-to-reward ratio. Do not set the target too far away to avoid missing out on profits due to a market reversal. Consider partial position closure as target levels are reached. This allows you to lock in some profits while leaving room for further growth.
Pending Orders:
- Place them at key support or resistance levels or when technical patterns form. Always set an expiration date for the order to prevent it from being triggered at an inappropriate time. Use in combination with stop-loss and take-profit orders for complete risk management. This allows you to automate your trading strategy and eliminate emotional influence on decision-making.
Common Mistakes and How to Avoid Them
Setting Stop-Losses Too Tight:
- This mistake often leads to prematurely closing potentially profitable trades. To avoid this, consider the average volatility of the asset and use technical analysis to determine the optimal level. Give your trade some “breathing room,” but don’t forget to maintain sensible risk management.
Overusing Market Orders:
- This can result in worse execution prices and increased trading costs. Try to use limit orders whenever possible, especially in less liquid markets or during periods of high volatility. This will help you get better prices and improve overall trading efficiency.
Ignoring Commissions:
- Small commissions can significantly impact profitability, especially with frequent trading. Always factor commissions into your calculations of potential profit and loss. Treat them as part of your trading strategy and adjust your target levels accordingly.
Reviews