Forex Trading: What It Is and How It Works
Forex trading is the global market for buying and selling currencies. It is the largest and most liquid financial market in the world. In this article, you will find an answer to the most important question among traders: What is Forex trading, and how does it work? Let’s explore it step by step.
Contents
- 1 What Is Forex Trading?
- 2 How Does Forex Trading Work?
- 3 How Forex Trading Works in Practice?
- 4 Is Forex Trading Profitable?
- 5 Does Forex Trading Really Work?
- 6 Can You Make Money Trading Forex?
- 7 Final Thoughts
What Is Forex Trading?

Forex trading, also known as foreign exchange or FX trading, is converting one currency into another. The amount of currency that is converted every day can cause price movements in some currencies to be extremely volatile, which is something that traders should be aware of before they start forex trading.
FX is one of the most actively traded markets in the world, with individuals, companies, and banks carrying out around $6.6 trillion worth of forex transactions every single day.
These transactions happen in currency pairs, such as EUR/USD (Euro/US Dollar) or GBP/JPY (British Pound/Japanese Yen). Traders speculate on the price movements of these currency pairs to make a profit.
How Does Forex Trading Work?
So, now that we know the definition of forex trading, let’s find out how it works.
Currency Pairs
Every forex trade involves two currencies. The first currency is the “base,” and the second is the “quote.” For example, in the EUR/USD pair, EUR is the base, and USD is the quote.
What Is a Forex Pair?
A forex pair is a combination of two currencies that are traded against each other. There are hundreds of different combinations to choose from, but some of the most popular include the euro against the US dollar (EUR/USD), the US dollar against the Japanese yen (USD/JPY), and the British pound against the US dollar.
The primary currency (base) is always positioned to the left of a currency pair, while the secondary currency (quote) is always to the right. The primary currency is always equal to one, while the secondary currency is equal to the current exchange rate of the pair — indicating the number of secondary currency units required to purchase one unit of the primary currency. Therefore, when engaging in currency trading, you are essentially selling one currency to purchase another.
Currency Codes and Their Nicknames
Every currency in forex trading is signified by three letters, known as the ISO 4217 Currency Codes. These codes make it easy to identify currencies worldwide. The first two letters represent the country of origin, while the third letter signifies the currency’s name. For example, AUD stands for the Australian dollar, and USD represents the United States dollar.
These codes are essential in forex trading as they ensure uniformity and clarity in the global market. Traders often use nicknames for popular currency pairs, such as the USD, which is often referred to as the “Greenback” due to its green-colored notes. The AUD is also known as the “Aussie”. Understanding these codes and nicknames can help traders navigate the forex market more easily.
Fout Types of Currency Pairs
- Major Pairs. These are the seven most traded currencies, making up around 80% of global forex trading. Common examples include EUR/USD, USD/JPY, GBP/USD, and USD/CHF.
- Minor Pairs. These are less frequently traded pairs, usually involving major currencies against each other, rather than the US dollar. Examples include GBP/CAD, EUR/CHF, and GBP/JPY.
- Exotic Pairs. These pairs consist of a major currency paired with a currency from a smaller or emerging economy. Examples include USD/MXN, EUR/ZAR, and GBP/SGD.
- Regional Pairs. These pairs are classified based on regions, such as Scandinavia or Australasia. Examples include EUR/NOK, AUD/NZD, and AUD/SGD.
Most forex transactions are conducted by banks or individuals aiming to buy a currency that will increase in value relative to the one they sell. For instance, if you’ve ever exchanged currencies while traveling, you’ve participated in a forex transaction.
What Is the Spread in Forex Trading?
In the context of foreign exchange trading, the spread is the disparity between the bid price (the price at which a trader can sell a currency pair) and the asking price (the price at which a trader can buy a currency pair). The spread represents the expense of trading and is how forex brokers typically generate income without charging explicit fees.
Types of Spreads
- Fixed Spread: The difference between the bid and ask prices remains constant, regardless of market volatility. This is common with market maker brokers.
- Variable Spread: The difference fluctuates depending on market conditions, such as liquidity and volatility. This is more common with Electronic Communication Network (ECN) brokers.
How It’s Measured
- Spreads are measured in pips, the smallest price movement in a currency pair. For example, if the EUR/USD bid price is 1.2000 and the asking price is 1.2003, the spread is 3 pips.
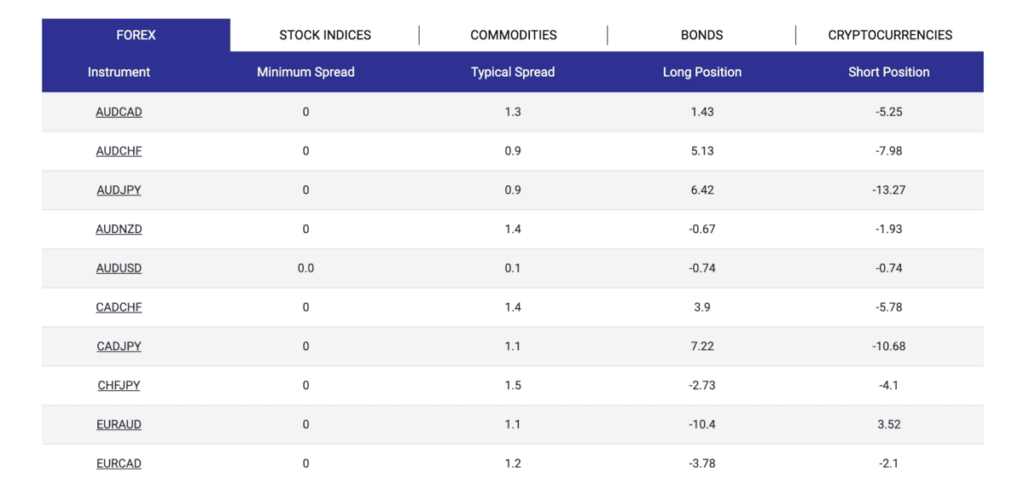
Factors Influencing the Spread
- Market Volatility: During periods of high volatility, such as during economic news releases, spreads can widen.
- Liquidity: Highly traded currency pairs like EUR/USD generally have tighter spreads, while exotic pairs with lower liquidity may have wider spreads.
- Broker Type: ECN brokers typically offer tighter spreads but may charge a commission, whereas market makers include their fees within the spread.
Why the Spread Matters?
The spread directly affects a trader’s profitability. For example, if a trader buys a currency pair, they start the trade with a slight loss, because they must overcome the spread in order to break even. Alternatively, narrow spreads are preferable for traders, particularly for high-frequency and day trading strategies. Understanding the spread is essential for managing costs and optimizing trading strategies in the foreign exchange market.
Exchange Rate
The price of a currency pair is determined by the exchange rate, which shows how much of the quoted currency is needed to buy one unit of the base currency.
The exchange rate is the value of one currency to another currency. It determines how much of one currency you can exchange for another. For example, if the exchange rate between the US dollar (USD) and the euro (EUR) is 1 USD = 0.92 EUR, this means that for every US dollar, you would get 0.92 euros.
There are two main types of exchange rates: fixed and floating. Exchange rates fluctuate due to various factors, including supply and demand, economic indicators, political stability, and market speculation.
Market Players
Forex traders include banks, financial institutions, corporations, and individual retail traders. They participate in the market for various reasons, such as hedging, speculation, or international business.
- Central banks, such as the Federal Reserve, European Central Bank, and Bank of Japan, play a crucial role in shaping currency values. They achieve this by adjusting interest rates, implementing monetary policies, and directly intervening in the market to stabilize their economies.
- Commercial banks, on the other hand, act as intermediaries, facilitating forex transactions for their clients, including multinational corporations, governments, and individual traders. They also engage in forex trading for profit.
- Investment banks are involved in large-scale forex trading, particularly in the interbank market. They assist large businesses and investors in managing currency risk.
- Hedge funds utilize the forex markets to generate profits through speculative trading. They often employ high-risk, high-reward strategies, using leverage.
- Corporations — Multinational enterprises engage in foreign exchange trading to mitigate the risk of currency fluctuations when conducting international transactions or to protect against currency volatility.
- Individual Investors — These are retail traders who participate in forex trading through online platforms, employing either technical or fundamental analysis to inform their trading decisions.
- Intermediaries — Forex brokers act as intermediaries between retail traders and the broader market, providing trading platforms and access to the forex market. They generate revenue through spreads or commissions.
- Governmental Entities — Governments can impact the market through fiscal policies, international trade policies, and by collaborating with central banks to influence exchange rates.
Margin and Leverage in Forex Trading
Forex brokers offer leverage, enabling traders to control larger positions with a smaller initial investment. While leverage can amplify profits, it also significantly increases the potential for losses.
Margin refers to the initial deposit required to open and maintain a leveraged position. For instance, a trade on the EUR/USD currency pair might only require a margin of 0.50% to initiate. This means that instead of needing $100,000 to open a position, you’d only need to deposit $500.
How Forex Trading Works in Practice?
Forex trading happens in the over-the-counter (OTC) market, meaning trades are conducted directly between participants rather than through a centralized exchange. Here’s a practical example:
- A trader believes the Euro will strengthen against the US Dollar.
- They buy the EUR/USD pair at an exchange rate of 1.2000.
- If the exchange rate rises to 1.2100, the trader can sell the pair for a profit.
- If the rate falls, the trader incurs a loss.
Is Forex Trading Profitable?
Forex trading can be profitable, but it does come with certain risks. Success requires not only a solid trading strategy but also the knowledge of market trends and economic indicators, as well as effective risk management techniques, such as using stop-loss orders to limit potential losses.
While some traders make significant profits, others may lose their capital due to market volatility or lack of experience. It’s crucial to approach forex trading with a clear understanding of its complexities.
Does Forex Trading Really Work?
Forex trading really works, but it’s not a guaranteed way to make money. The market’s efficiency and high liquidity offer opportunities for gains, but they also mean that prices can fluctuate rapidly. Successful traders rely on:
- Technical analysis to identify patterns and trends
- Fundamental analysis to understand the impact of economic events
- Discipline to stick to their trading plan
Before starting trading Fx, you should choose the right broker. For example, RoboForex provides access to popular platforms such as MetaTrader 4 (MT4), MetaTrader 5 (MT5), and cTrader, all of which offer robust technical analysis tools. These platforms include a wide range of charting options, technical indicators, drawing tools, and advanced chart studies (e.g., Fibonacci, trend lines, moving averages, Bollinger Bands, RSI, MACD).
Along with popular MT4 and MT5 platforms, Tickmill also offers TradingView integration, which provides a more advanced charting experience for traders who prefer more detailed analysis.
Can You Make Money Trading Forex?
You can make money trading forex, however, it involves predicting the movement of currency pairs and requires skill, knowledge, and strategy. Traders aim to profit by speculating on the exchange rate fluctuations between two currencies, either going long (buying the base currency) when they expect the base currency to strengthen against the quote currency or going short (selling the base currency) when they expect it to weaken.
When the price of a forex pair is rising, it indicates that the base currency is strengthening against the quote, meaning more of the quote currency is required to buy one unit of the base. Conversely, if the price is falling, the base currency is weakening, and fewer quote units are needed to buy one of the base currency.
There are various forex trading styles, such as scalping, day trading, swing trading, and position trading, which can be chosen depending on whether you have a short-term or long-term outlook. Nevertheless, it’s important to remember that forex trading carries significant risks, and without careful analysis and risk management, it’s possible to lose money as well.
Final Thoughts
Forex trading is a dynamic activity that has become extremely popular these days. However, you should be careful when trading Forex, as it requires a combination of knowledge, strategy, and emotional discipline.
Whether you’re a novice or an experienced trader, it’s essential to understand the fundamentals of forex trading. If you’re considering entering the market, choose a reputable Forex broker, spend time understanding how Forex trading works, practice on a demo account and develop a trading plan. With patience and perseverance, you can explore the exciting world of Forex and its opportunities.
Reviews